058-函数指针
函数指针就是将函数赋值给一个变量的方法
这节的函数指针是继承自c的
Java8中也有这样的操作
import java.util.function.Function;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Function<Integer, Integer> function = Hello::testFunction;
int result = function.apply(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
private static int testFunction(int param) {
return param * 2;
}
}
#include <iostream>
void hello() {
std::cout << "Hello World" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
auto fun = hello;
fun();
fun();
fun();
return 0;
}
我们可以使用auto来让编译器推断类型,并将hello函数赋值给fun变量,并对其进行调用
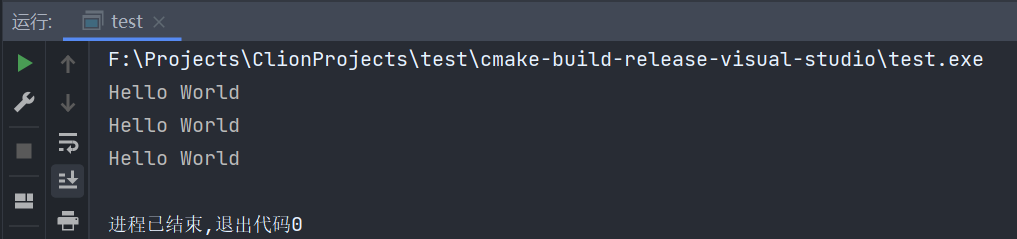
它的实际类型为void (*)()
我们定义函数指针的方式为
返回类型 (*名称)(一堆参数的类型)
我们可以使用具体类型来接受或者使用typedef来进行定义并赋值调用
#include <iostream>
void hello() {
std::cout << "Hello World" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
//我们可以通过实际的类型来接收它,而不是auto
void (*fun)() = hello;
fun();
fun();
fun();
//也可以使用typedef来定义
typedef void (*HelloFunction)();
//创建函数指针
HelloFunction function = hello;
function();
function();
function();
return 0;
}
我们还可以尝试为函数添加参数,像下面这样
#include <iostream>
void hello(int value) {
std::cout << "Hello World, value = " << value << std::endl;
}
int main() {
void (*fun)(int) = hello;
fun(9);
fun(0);
fun(3);
return 0;
}
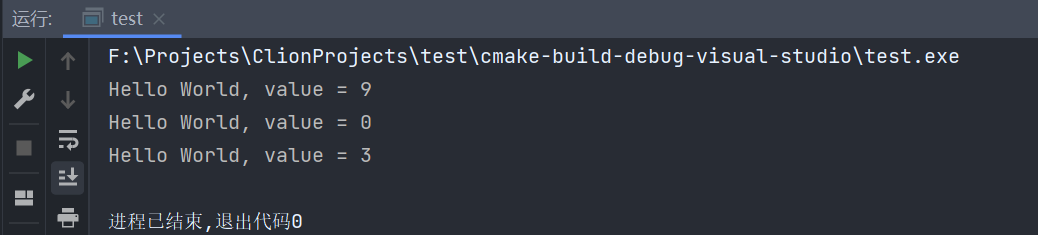
在Java中,我们可以这样写
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(9, 9, 0, 9, 0, 3);
list.forEach(Hello::sout);
}
private static void sout(int value) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
我们使用函数指针,一样的,可以这样写
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
void foreach(const std::vector<int> &vector, void (*fun)(const int &)) {
for (int obj: vector) {
fun(obj);
}
}
void print(const int &value) {
std::cout << value << std::endl;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> vector = {9, 9, 0, 9, 0, 3};
foreach(vector, print);
return 0;
}
在java中,我们可以使用lambda表达式
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(9, 9, 0, 9, 0, 3);
list.forEach(value -> System.out.println(value));
}
}
在这里一样的
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
void foreach(const std::vector<int> &vector, void (*fun)(const int &)) {
for (int obj: vector) {
fun(obj);
}
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> vector = {9, 9, 0, 9, 0, 3};
foreach(vector, [](const int &value) { std::cout << value << std::endl; });
return 0;
}